Micro Economics – Analysis on the Behavior and Performance of Firms
Micro economics
QUESTION ONE
Perfect Competition:
Perfect competition is a market place or structure where many companies offer a similar product. As there is free choice of entry and exit and perfect information. Therefore companies will make normal profits and prices will be kept low by pressure of the competition in the market. All companies even the new trader are expected to have equal entree to resources and developments in production technologies achieved by any other company.
Features:
- Number of firms:
Number of firms, with perfect competition increasing in the boundary as there can be infinity number of companies in one market selling the similar product.
- Product Differentiation:
Product differentiation is the method of dissimilar a product or service from others to make it more unique and attractive to a target market. As this occurs because buyers notice a difference between products. However as the product becomes more different, which changes the category of each product and putting them into a category will become more difficult, and the product attracts less comparisons with its competition.
- Control over price
As there is acompetition in the market, and each individual has strong assumptions and expectations. Many individual buyers, therefore there is a slight or none control over the price or quantity.
- Extent of market information
There are no barriers to exit for the companies. Companies are free exit the market at their freedom of choice.
- Freedom of entry:
As there is freedom of entry and perfect information, there are no barriers to entry for firms. Firms are free to enter the market at their choice.
QUESTION TWO
- Short Run

- Long Run

QUESTION THREE
Monopoly
In a monopoly Competitive markets each firm makes their own decisions about the price and output, based on their own product, its market, and itscosts of manufacture.Monopoly competitive is a place where an individual owns all or most of the market for their own individual product or services. Less competition in the market will always result in high price and inferior products.
Features
- Number of firms
In monopoly there is only one firm in the market, which has the high market power.
- Product Differentiation
In a monopolistically competitive market there is a significant amount of non-pricecompetition. As a result product differentiation is key for any monopolistically competitive firm, it is a process of unique product or service from others to make it more attractive to a target market. Differentiation happens because consumersnotice a difference.

- Control over price
As a there is only one company in the Market, it means the company has full control over the market, also has own terms and condition. As the company is branded by many firms selling products that are not identical, therefore the company can choose its own price to sell that product.
- Extent of market information
There are barriers to when exiting a monopoly market. As if government believes that the product provided by the monopoly is important for well-being of the public, then the monopoly will not be allowed to leave the market for example Healthcare products. This barrier to exit is always or mostly applied to publics’ everyday services or benefits, such as electricity companies, local telephone companies and etc. These are mostlyconsiderednecessary services that cannot be stopped without permission from a government regulation authority.
- Freedom of Entry
As a monopoly is normally certain of being the only firm in a market because of various barriers to entry. Some of the key barriers to entry are:
- government license or franchise,
- resource ownership
- patents and copyrights
- high start-up cost
QUESTION FOUR
- Short Run

- Long Run
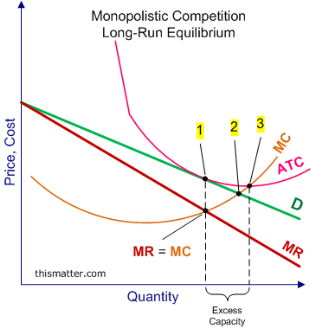
QUESTION FIVE
Market Power
In economic science and significantly in industrial organization, market power is that the ability of a firm to fruitfully raise the value of a decent or service over cost. In utterly competitive markets, market participants don't have any market power.
- Barriers to entry
Barriers to entry are designed to block potential entrants from coming into a market productively. They request to shield the monopoly power of existing corporations in associate business and so maintain supernormal (monopoly) profits within the end of the day. Barriers to entry have the impact of creating a market less debatable
- Product differentiation
Product differentiation is that the method of identifying a product or service from others to create it a lot of engaging to a target market.
- Price Discrimination
A monopolize is also ready to interact in a very policy of value discrimination. This happens once a firm charges totally different or special value to different teams of shoppers for a uniform sensible or service, for reasons not related to the prices of production. It’s necessary to worry that charging totally different costs for similar merchandise isn't value discrimination. As an example, value discrimination doesn't occur once a rail company charges a better value for a primary category seat. As a result of the value premium over an inferior seat can be explained by variations within the price of providing the service.
QUESTION SIX
Monopolistic Competition
The model of noncompetitive competition describes a standard market structure within which corporations have several competitors, however all sells a rather totally different product
Features
- Numbers of firms
There square measure giant numbers of companies commercialism closely connected, however not consistent merchandise. Every firm acts severally and includes a restricted share of the market. So, a private firm has restricted management over the market value. Sizable amount of companies ends up in competition within the market.
- Product Differentiation
Each firm is in an exceedingly position to exercise some extent of monopoly (in spite of enormous range of sellers) through product differentiation. Product differentiation refers to differentiating the product on the idea of name, size, colour, shape, etc. the merchandise of a firm is shut, however not good substitute of different firm.

- Control Over Price
A firm underneath noncompetitive competition is neither a price- taker nor a price-maker. However, by manufacturing a singular product or establishing a selected name, every firm has partial management over the worth. The extent of power to manage worth depends upon however powerfully the patrons’ area unit hooked up to his whole.
- Extent of market information
Buyers and sellers don't have good data concerning the market conditions. Merchandising prices produce artificial superiority within the minds of the shoppers and it becomes terribly troublesome for a shopper to judge totally different product on the market within the market. As a result, a specific product (although extremely priced) is most well-liked by the shoppers although different less priced product square measure of same quality
- Freedom of Entry
Under noncompetitive competition, companies area unit liberal to enter into or exit from the trade at any time they want. It ensures that there are a unit neither abnormal profits nor any abnormal losses to a firm within the end of the day. However, it should be noted that entry beneath noncompetitive competition isn't as simple and free as beneath excellent competition.
QUESTION SEVEN
- Short Run

- Long Run

QUESTION EIGHT
Oligopoly
In the market place an Oligopoly has a market structure eith few companies, however those few companies are leading companies in this market structure. This is extremely focused when market is shared with leading companies. Also small firms will try to operate in the same market. Although only a few firms dominate, it is possible that many small firms may also operate in the market.
Features:
- Number of firms
In Oligopoly there are few but leading companies in the market.
- Product Differentiation
In this market structure similarproducts are producedwith a few manufacture in the industry. However each manufacture attempts to make slightly different product in order to charge higher price to its consumers. .
- Control over Price
In the market Oligopolistsare price focused and there are many leading companies, so they will use predatory pricing to force rivals out of the market. Which means keeping theirprices artificially low, this can be below the full cost of production.
- Extent of Market Information
As this is market structure is dominated by small number of large firm, as these firms are quite large in size compared to overall size of the market. This creates significant market control, therefore extent of market control is depending on the number and size of the firms.
Freedom to entry
Oligopolies often maintain their placeof control in a marke, this might be because it is too expensive and also it is hard for possiblecompetitors to enter the market. Therefore there are barriers to entry in an Oligopoly which can stiff them purposely.
ƒ˜ Economies of large scale production
ƒ˜ High set-up costs
ƒ˜ High R&D costs

Q9. Explain the behaviour of oligopoly in terms of market structure
Price to explain stuck other . if one company change their way of selling their products , then it also effect the working of other similar company .
- Price leadership : in price leadership price of the product is decided by the then alternatively ,the other comparative company have decreased to sell their products.
- Kinked demand curve model: the kinked demand curve theory is an economic theory regarding oligopoly and monopolistic competition when it was created the idea fundamentally challenged classical economic tenets such as efficient markets and rapidly changing prices ideas that underlie basic supply and demand models. Kinked demand was an initial attempt to explain sticky price
- Behaviour.
- Advertising : Yes the company advertise to convince the customer so that they will buy their product. they spend allot of money on advertising.
- Output: there is competition between the countries if we take the example of OPEC like, in Arab country they sell mortal oil and the world price of oil will remain same.
- Product Differentation: There is great product differentiation in oligopoly
Q11. Using as an example of New Zealand’s Pharmaceutical Management Agency (PHARMAC) evaluate and describe how government regulation restrict the market power of firms.
A response was required, and in 1993 the Pharmaceutical Management Agency (PHARMAC) was created to actively manage Government disbursal on medicines.
PHARMAC’S objective was to introduce price battle to a market wherever it had not antecedent existed.
Pharmacy’s role was, in effect, to urge higher price for medicines so the most effective health outcomes may well be achieved from public cash pay on medicines.
From Pharmacy’s creation, there was potential for value reductions through the introduction of price battle between pharmaceutical corporations. Reference evaluation, a policy wherever grant levels for medication with similar effects are set at an equivalent level, was a big strategy in achieving lower costs.
All of those mechanisms facilitate cut back the number we have a tendency to pay money for medicines, generating savings that are ready to be accustomed subsidise a lot of merchandise – increasing New Zealanders’ access to medicines.
Pharmacy’s getting power has tripled since 1993. This implies that we are able to currently subsidise concerning 3 times the number of medicines that would be brought with equivalent cash in 1993.
Q12 Ans . In this graph average total cost increased quickly with the increase of quantity and then it started decreasing . Fixed cost remain fixed whether the output increased or decreased. marginal cost and variable cost it increased slowly with the increase of output. And last total cost has rapidly increased with the increase of quantity.
Q13. In this graph average cost of products decreased with the increase in the production as the cost of per product was $12 when the production was 1000. But when the production increased from 1000 to 200000 the price declined to $6 per unit.
Cite this page
Micro Economics - Analysis on the Behavior and Performance of Firms. (2017, Jun 26).
Retrieved March 9, 2026 , from
https://studydriver.com/micro-economics-analysis-on-the-behavior-and-performance-of-firms/
Stuck on ideas? Struggling with a concept?
A professional writer will make a clear, mistake-free paper for you!
Get help with your assignmentLeave your email and we will send a sample to you.
Perfect!
Please check your inbox